What is the purpose of the secondary air pump?
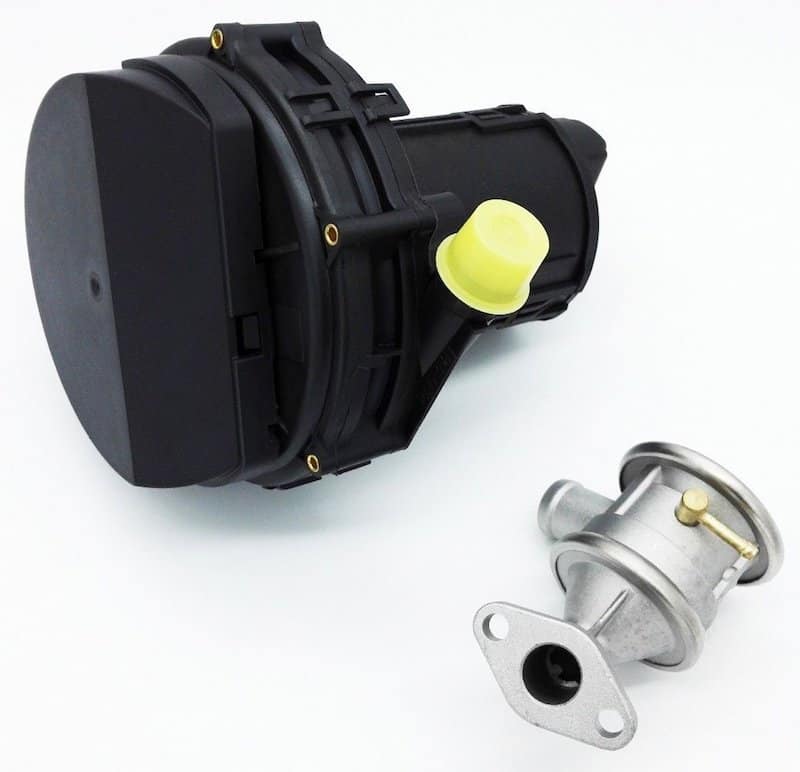
The primary purpose of the secondary air pump (SAP) is to reduce harmful emissions. Hydrocarbon (HC) and Carbon monoxide (CO) gasses are the two main gasses which contribute to smog.
Another noteworthy purpose of the secondary air pump is to prevent damage to the exhaust system by blowing out any accumulated water vapor that could freeze the system. This function is necessary when the system detects the ambient air is below -10 degrees C (-14 degrees F).
How does the secondary air pump work?
Immediately following a cold engine start (40 degrees C (104 degrees F) or below), injection of ambient air from the engine bay is directed to each exhaust manifold through a one-way valve. Due to this burst of air, hydrocarbons will oxidize quickly until the catalytic converter warms up. This will result in cleaner emissions on cold starts where vehicles usually run rich due to unburned fuel.
What is the purpose of the one-way valve?
The primary purpose of the one-way valve is to ensure fresh air only enters the exhaust manifolds. Possible backfire could enter up the pipes without the valve and potentially damage the air pump when there is no vacuum.
How does the one-way valve function?
There is a control module which activates the vacuum vent valve whenever the air pump is activated.
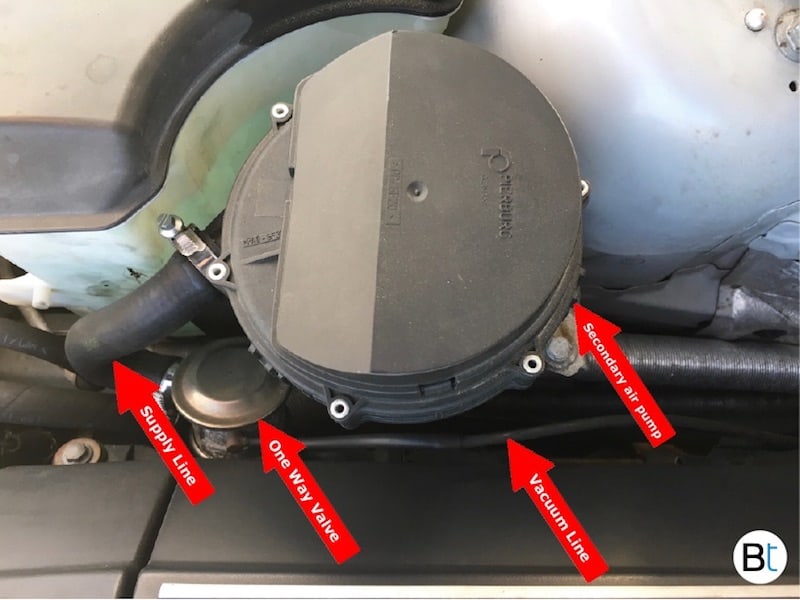
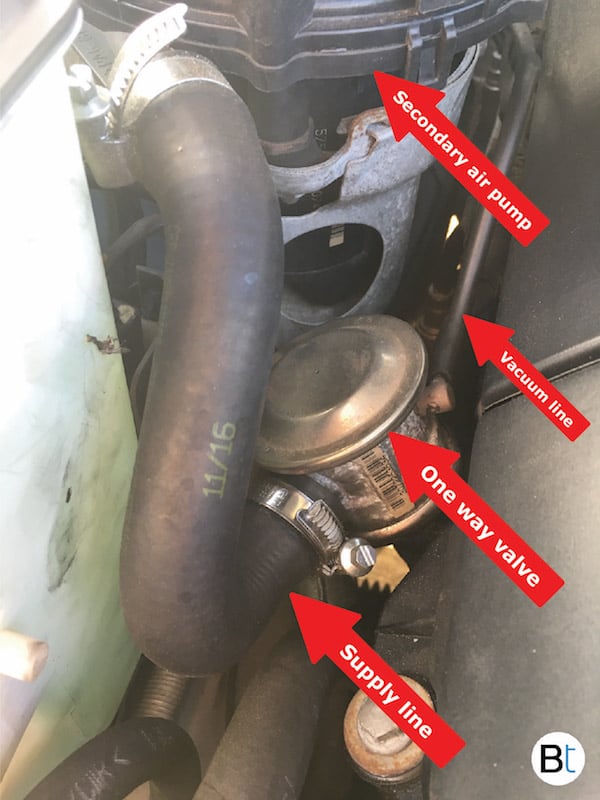
Once the vacuum vent valve becomes energized, a vacuum is applied to the non-return valve which allows air to be injected into the exhaust manifold through the pump. A vacuum is retained in the lines, by the use of a check valve, in order to allow the non-return valve to be immediately activated on cold engine start up. If the vacuum / vent valve is inactive, the vacuum to the non-return valve is removed and is vented to atmosphere.
How is the secondary air pump monitored?
Monitoring of the SAP is through the oxygen sensor located before the catalytic converter. This pre cat sensor should sense a lean condition as a result of the pump working. If the oxygen sensor signal does not change to a lean condition within 120 seconds, a fault code will be set to identify the faulty banks. Upon a second cold start, if the oxygen sensor still does not sense a lean condition, the Check Engine light will turn on.
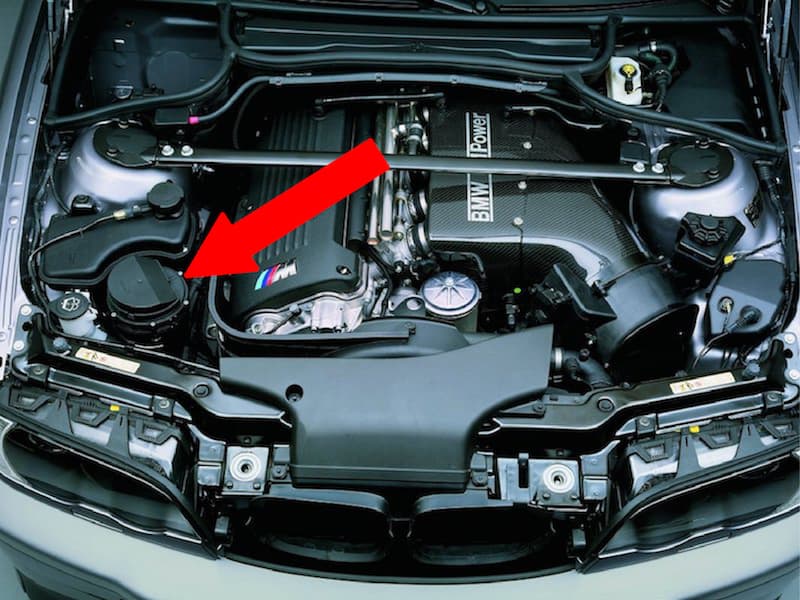
Where is the secondary air pump located?
The secondary air pump is usually located on the passenger side of the engine bay near the front of the vehicle. Refer to the images below for the typical location.
What are the benefits of the secondary air pump?
➊ Reduce emissions.
➊ Reduce warm-up time of the catalytic converter.
What are common symptoms of the failing secondary air pump system?
➊ Noisy / faulty bearings inside the pump.
➋ Cracked, broken, dry rotted vacuum line.
➌ Cracked, broken, dry rotted air supply line.
➍ Clogged one-way valve due to carbon build up.
Can I remove the secondary air pump?
Yes, the removal of the secondary air pump is possible. The benefits are: reduce weight, clean up your engine bay and to simplify troubleshooting by removing a system. The installation of a blanking plate where the one-way valve used to sit is a requirement. Another necessity is the reprogramming of the ECU, which accounts for the removal of the SAP system in order to not throw any fault codes. Note that this removal will affect your vehicle's emissions and may not allow your vehicle to pass smog test.
Where can I learn more BMW fun facts?
Learn more BIMMERtips fun facts by clicking HERE